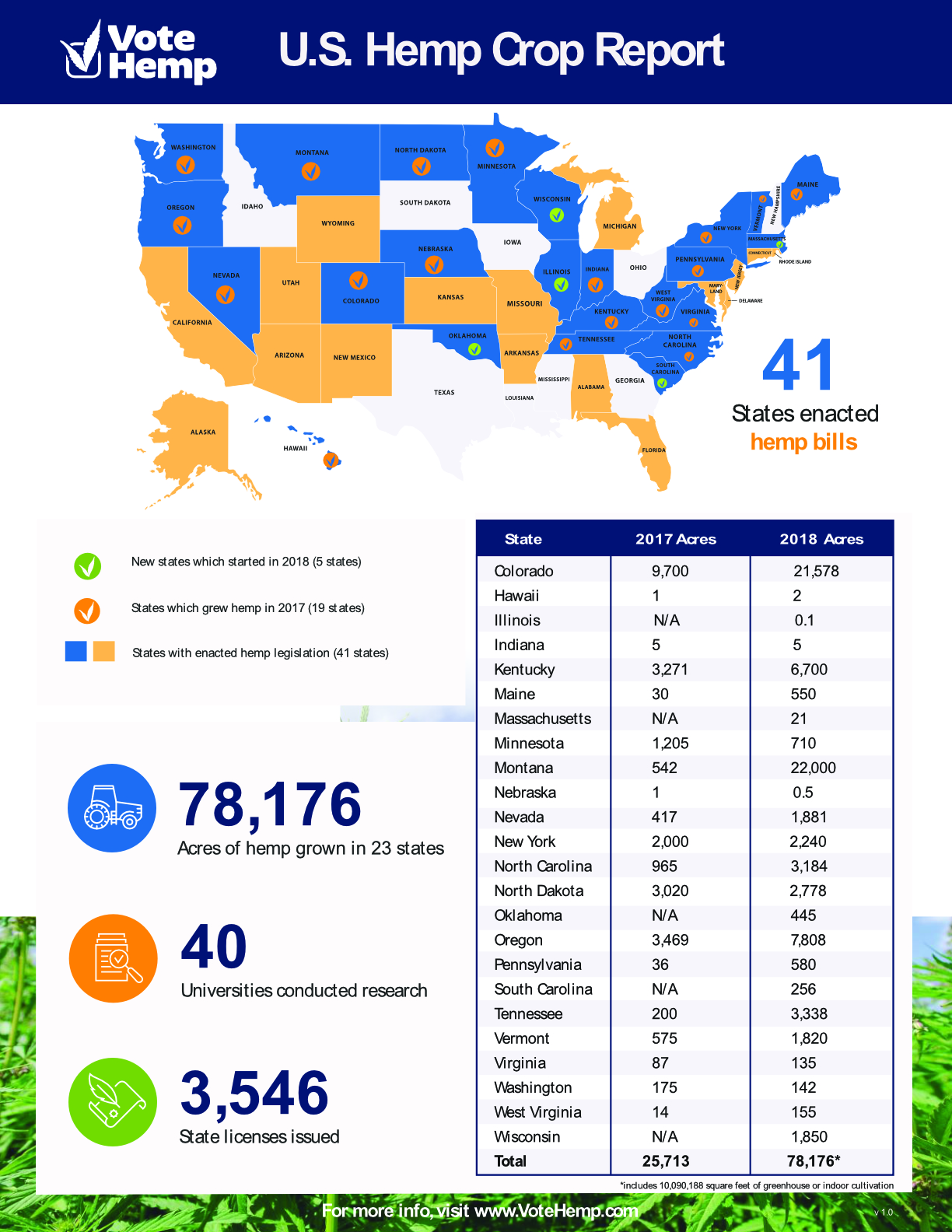
WASHINGTON — The area planted to hemp in the United States increased to 78,176 acres in 2018 from 25,713 acres in 2017, according to a crop report from Washington-based Vote Hemp, a hemp advocacy organization. The natural foods industry is one of the fastest growing categories for hemp use as it contains omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids, fiber protein, vitamin E and iron, according to Vote Hemp.
The Agricultural Improvement Act of 2018, also known as the farm bill, removed hemp from the Controlled Substances Act, which cleared the way for the cultivation, production or commercial activity in the United States for products that contain hemp or constituents of hemp. While hemp and marijuana both are classified as cannabis, hemp contains 0.3% or less of the psychoactive compound delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (T.H.C.).
“We’ve seen hemp cultivation significantly expand in the U.S. in 2018, with over triple the number of acres planted in hemp compared to last year and the addition of four more states with hemp programs,” said Eric Steenstra, president of Vote Hemp. “Now that we have lifted federal prohibition on hemp farming, it’s time to invest our energy in expanding hemp cultivation and the market for hemp products across the country so that all can reap the benefits of this versatile, historic American crop.”
Hemp was grown in 23 states in 2018. Montana led the way at 22,000 acres, up from 542 acres in 2017. Colorado rose to 21,578 acres from 9,700 acres. Forty universities conducted research on hemp in 2018. Besides foods and beverages, other potential uses for hemp include batteries and packaging materials.