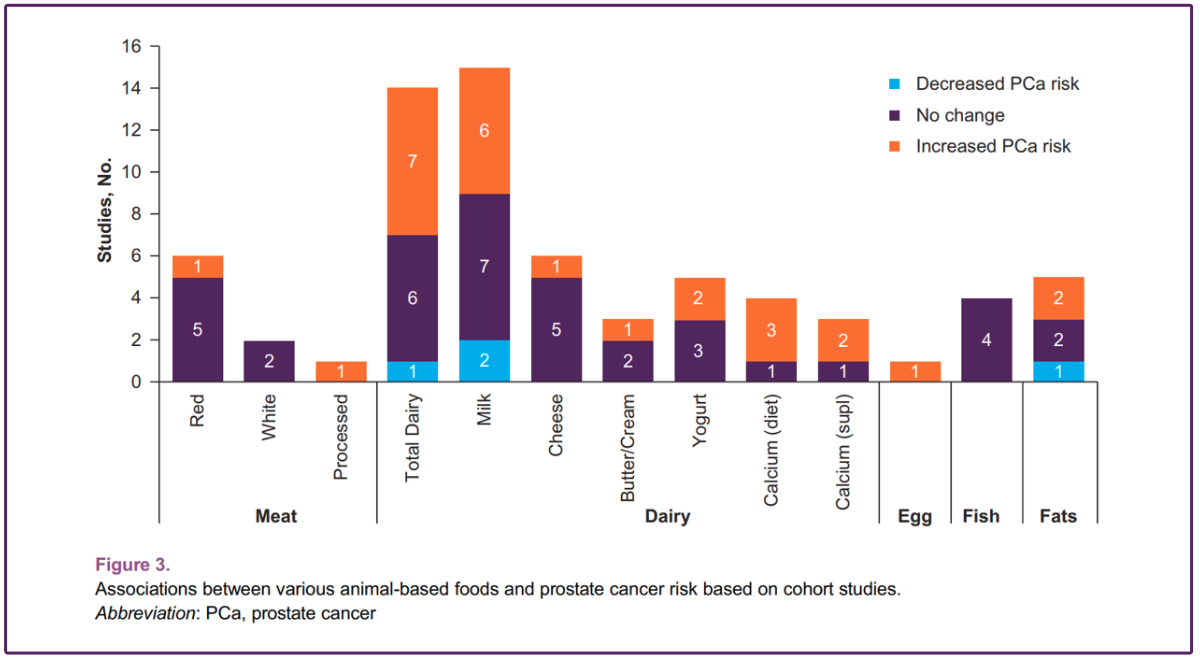
CHICAGO — High consumption of dairy products may be linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer, according to a recent study published in The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association.
In the study, researchers from the Mayo Clinic said previous reports have shown dairy products are the primary source of calcium in Western countries, where prostate cancer rates are high. Rates are lower in Asian countries, which also have lower levels of dairy consumption. Increased calcium intake also was linked to increased prostate cancer risk, leading researchers to conclude that calcium may play an important role in the link between dairy and prostate cancer.
The study found no clear association of increased risk of cancer linked to other animal-based foods, though it did identify a decreased risk associated with plant-based diets.
“Our review highlighted a cause for concern with high consumption of dairy products,” said John Shin, Ph.D., an oncologist at the Mayo Clinic and lead author of the study. “The findings also support a growing body of evidence on the potential benefits of plant-based diets.”
The research reviewed 47 studies published over the last dozen years, totaling more than 1 million participants. While patterns of association between prostate cancer risk and dairy consumption emerged, more investigation is needed to understand the nature and strength of the association, Dr. Shin said.
Another recent study from the Journal of the American Heart Association also found support for the health benefits of plant-based diets. The study found diets emphasizing higher intakes of healthy plant foods were associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, death from cardiovascular disease and death from all causes.
The study in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association can be found here, and the study from the Journal of the American Heart Association can be found here.




